Understanding Bone Density Tests: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
As we go through life, our bones play an essential role in providing structure, protecting organs, and supporting our overall well-being. However, as we age, the risk of bone-related conditions such as osteoporosis increases. To evaluate the strength and density of our bones, medical professionals recommend a bone density test. In this article, I will provide a comprehensive understanding of bone density tests, their significance, the procedure involved, and offer suggestions to maintain optimal bone health.
1. Why Bone Density Tests Matter
Bone density tests, also known as bone mineral density (BMD) tests, are crucial in assessing the strength and health of our bones. These tests help identify conditions like osteoporosis, which weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. By measuring the amount of mineral content in the bones, bone density tests offer insight into the risk of fractures and provide a basis for diagnosis and treatment planning.
2. Who Should Consider Bone Density Tests
While bone density tests are commonly associated with older adults, they can be relevant for individuals of varying age groups. People who fall into the following categories should consider discussing bone density testing with their healthcare providers:
2.1 Women Entering Menopause
Menopause causes a decline in estrogen levels, which can accelerate bone loss. Women who are postmenopausal or nearing menopause may benefit from bone density tests to assess their bone health and detect early signs of osteoporosis.
2.2 Individuals with Risk Factors
Certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing osteoporosis. These include a family history of osteoporosis, a history of fractures, being of Caucasian or Asian descent, a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and the prolonged use of medications such as corticosteroids. Individuals with these risk factors should consider bone density testing.
2.3 Those on Long-term Medications
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and anticonvulsants, can contribute to bone loss. If you have been prescribed long-term medications that may affect bone health, your healthcare provider may recommend regular bone density testing.
3. The Bone Density Testing Procedure
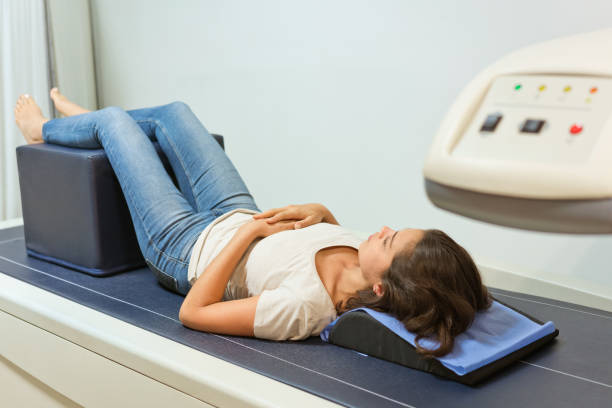
The most common method of bone density testing is the dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. The DEXA scan is a painless, non-invasive test that measures bone mineral density in specific areas of the body, most commonly the hip and spine. The procedure involves lying on a table while a scanning device passes over your body, emitting low-dose X-rays to measure bone density.
4. Interpreting Bone Density Results
Bone density test results are typically reported as T-scores and Z-scores. The T-score compares an individual’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult of the same sex, providing an indication of fracture risk. A T-score of -1.0 or above is considered normal, while scores between -1.0 and -2.5 suggest low bone mass (osteopenia). T-scores below -2.5 indicate osteoporosis.
Z-scores, on the other hand, compare an individual’s bone density to that of their age group, providing information on bone density in relation to peers. Z-scores significantly below the average for the age group may indicate the need for further evaluation.
5. Strategies to Enhance Bone Health
To maintain strong and healthy bones, it is crucial to adopt a proactive approach. Here are some strategies that can contribute to enhancing bone health:
5.1 Balanced Diet
A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients is fundamental for bone health. Incorporate dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds into your diet to ensure an adequate intake of bone-strengthening nutrients.
5.2 Regular Exercise
Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, dancing, and strength training, can help improve bone density and strength. Engaging in physical activity regularly can reduce the risk of bone loss and fractures.
5.3 Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to bone loss and weaken bone strength. Minimizing or avoiding these habits altogether can help preserve bone health.
5.4 Fall Prevention
Falls are a significant cause of fractures, particularly among older adults. Taking preventive measures such as maintaining a clutter-free environment, installing handrails, and using appropriate footwear can reduce the risk of falls and subsequent fractures.
5.5 Discussing Medications with a Healthcare Provider
If you are taking medications known to affect bone health, discuss alternative options or potential supplements with your healthcare provider. They can guide you on mitigating the impact on your bones.
Conclusion:
Bone density tests are invaluable tools for assessing bone health and identifying conditions such as osteoporosis. By understanding the importance of bone density tests, their interpretation, and implementing preventive strategies, you can take charge of your bone health and minimize the risk of fractures and associated complications.
FAQs:
Q1: How often should I have a bone density test?
A: The frequency of bone density tests depends on various factors, including your age, risk factors, and previous test results. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate testing schedule for your situation.
Q2: Are bone density tests painful?
A: No, bone density tests, especially the DEXA scan, are painless and non-invasive. The procedure involves lying still on a table while the scanning device passes over your body.
Q3: Can I have a bone density test if I’m pregnant?
A: Bone density tests, particularly those involving X-rays, are not recommended during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus. If you are pregnant or suspect you might be, inform your healthcare provider before undergoing any testing.
Q4: Can men benefit from bone density tests?
A: Absolutely. While osteoporosis is more commonly associated with women, men can also develop the condition. Men with risk factors such as age, family history, and certain medications should consider bone density testing.
Q5: Can I improve my bone density through lifestyle changes alone?
A: Adopting a bone-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and other preventive measures, can help improve bone density and overall bone health. However, in cases of osteoporosis, medical intervention may be necessary. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.